In today’s B2B landscape, especially in large-scale projects, ‘good service’ is no longer a subjective concept. Companies now demand more than just expertise; they expect written commitments regarding the speed and quality of that delivery. The quest for Enterprise Services SLA Benchmarks is the strongest evidence that the industry is moving toward full standardization.
Here is our comprehensive guide to taking your professional service agreements to the next level.
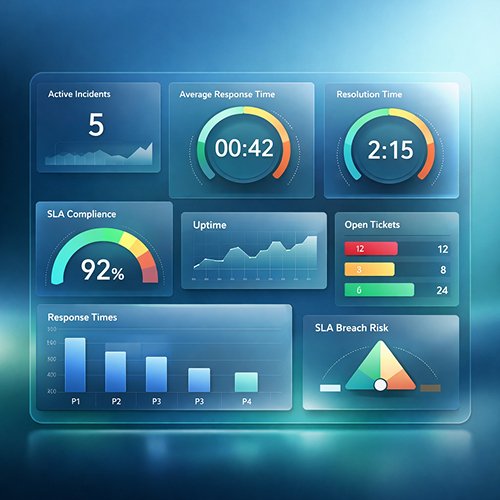
1. What are SLA Benchmarks and Why Are They Vital for Enterprise Services?
SLA Benchmarks involve comparing your service performance metrics (response time, resolution speed, error rate, etc.) against global best practices or industry standards.
Building Trust: Being able to tell a client, “We perform 15% above market standards,” significantly boosts your sales closing rates.
Operational Efficiency: It allows you to numerically identify exactly where your team is lagging or underperforming.
Risk Management: It prevents over-promising by setting realistic commitments, thereby reducing legal and contractual risks.
2. Deep Dive Metric Analysis: Enterprise Standards
Success in corporate service management is measured not just by completing the task, but by how strictly the process adheres to predefined SLA Benchmarks. In 2026 standards, transparent performance scoring is the cornerstone of a sustainable partnership for both service providers and clients.
When managing Enterprise Services, focusing on a single metric can be misleading. A true performance scorecard is formed by blending:
Critical response times,
Project delivery discipline (delay rates),
And CSAT data representing end-user satisfaction.
The following SLA Performance Score Calculator allows you to compare your current data with up-to-date SLA Benchmarks and standardize your service quality on a scale of 100.
Tip: In enterprise standards, a score of 95% and above is considered “Excellent,” 85-95% is “Room for Improvement,” and below 85% is “High Risk” (Potential Violation).
SLA Performance Score Calculator
SLA: Stop Manual Tracking, Switch to Dynamic Performance Management
In traditional professional services, SLA (Service Level Agreement) management is often built on ‘Excel reports prepared at month-end’ and ‘disputes over late penalties.’ However, in the 2026 landscape, Enterprise-level clients expect a proactive approach rather than a reactive one.
This is where SPIDYA transforms your Service Level Agreements (SLAs) from static documents into living, breathing performance mechanisms.
🔵 Intervene Before an "SLA Violation" Even Happens with SPIDYA Software!
SPIDYA’s smart workflows and Cheetah Low-Code infrastructure transform your contract clauses into digital auditors.
Burn-down Alerts: The system automatically notifies the team when 50% of the resolution time is reached, and alerts the manager at 80%. Bu allows for intervention before the issue hits the “red zone.”
Dynamic Benchmark Comparison: You can view real-time department-to-department or period-based benchmark analyses via SPIDYA Dashboards, helping you refine your Enterprise Services strategy.
Smart Workflows: In a construction site or a professional service process, a task approaching its SLA limit can be automatically reassigned by SPIDYA to the “most available expert.”
🔵 The SPIDYA Difference: XLA (Experience Level Agreement)
We don’t just look at whether the “problem is solved.” With SPIDYA, you can integrate Experience Level Agreements (XLA) into your metrics. You might resolve an issue within an hour (an SLA success), but if the user experience during that resolution was poor, it cannot be considered a true success. SPIDYA blends these two data points to provide you with a True Performance Score.
4. Advanced Strategies: The "Bonus-Malus" Era in SLAs
In modern enterprise services contracts, it’s no longer just about penalties (Malus); it’s also about rewarding success (Bonus).
Service Credits: If you commit to 99.9% uptime but deliver 99.0%, you provide a 10% discount on the customer’s next monthly invoice.
Early Delivery Premiums: In project-based professional services, delivering a critical phase ahead of the benchmark time and without errors earns small “success premiums.” This motivates the team and drives customer satisfaction to its peak.
5. IDE and Automation: How is SLA Tracking Managed Technically?
In modern professional services, tracking SLA Benchmarks is no longer data reported after the work is done; it is an automation process that begins on the production line—within the Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These integrated environments where developers write code ensure that SLA timelines are kept under control while still in the “coding phase.”
By integrating these technical workflows into your broader Enterprise Services strategy, you ensure that every line of code aligns with your delivery commitments from day one.
Why is IDE Integration Crucial?
When a bug is reported or a new feature is requested, the SLA clock starts ticking. The IDE (Integrated Development Environment) used by the developer works in sync with the central project management system, offering the following advantages:
Real-Time Effort Tracking: The moment a developer begins working within the IDE, the “Response Time” metric is automatically paused, and the “Resolution Time” is activated.
Contextual Alerts: Critical tasks approaching their SLA limit appear as visual warnings directly on the developer’s workspace (IDE interface). This allows them to stay focused without the need for context switching.
Automated API Triggers: Once the software is “committed” or deployed to the test environment, the SLA status is updated via APIs without requiring any manual intervention.
Automation Layers: From Manual to Smart Tracking
To move SLA tracking beyond Excel spreadsheets and transform it into an autonomous structure, a triple-layered architecture is utilized:
Data Source (IDE & Git): Where raw data from development activities—such as coding, reviews, and approvals—is collected.
Integration Layer (Webhooks/API): The bridge that transmits real-time actions from the IDE (e.g., moving a task to “In Progress”) directly to the central system.
Visualization (Custom Dashboards): Analytical screens where collected data is compared against SLA Benchmarks, providing predictive insights to anticipate potential delay risks.
Conclusion
“In the enterprise world, competition is built on being ‘the most reliable’ rather than ‘the cheapest.’ An SLA framework based on benchmark data is the ultimate testament to your brand’s commitment and professional integrity