Knowledge Base
Create a corporate knowledge base system with the knowledge base module and enable IT teams and users to instantly find the information they need; store all experience and information on the central platform!

Create a corporate knowledge base with the knowledge base module and enable IT teams and users to instantly find the information they need; store all experience and information on the central platform!
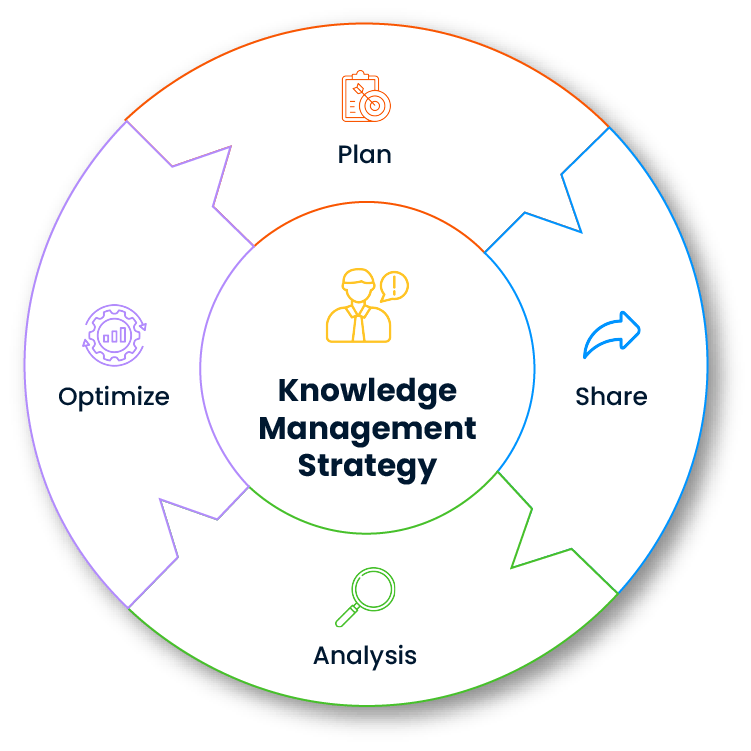
Benefits of the Knowledge Base Module

Collecting all technical knowledge and experience in a central knowledge base system prevents information loss within the organization. Even new team members can adapt quickly by accessing past incidents and solution methods. This approach makes knowledge management processes sustainable.

Users can directly access guide articles to solve their problems. This reduces support requests and eases the burden on IT teams. In this way, the knowledge base system enables both end users and technical teams to use their time efficiently.

Information circulation within the team is supported through article sharing and user feedback. Organizational learning is kept alive by updating content according to developing needs. The knowledge base system accelerates development by automating this cycle.
Standard solutions for common problems are collected on a single platform. In this way, consistent, accurate and fast information can be presented. The module directly affects user satisfaction and service quality.

Each knowledge article is tracked through version control, and it can be tracked by whom it was created or updated. This prevents the spread of misinformation and clarifies areas of responsibility. This transparency increases the reliability and accuracy of the knowledge base system.
Collecting all technical knowledge and experience in a central knowledge management prevents information loss within the organization. Even new team members can adapt quickly by accessing past incidents and solution methods. This approach makes knowledge management processes sustainable.
Users can directly access guide articles to solve their problems. This reduces support requests and eases the burden on IT teams. In this way, the knowledge management enables both end users and technical teams to use their time efficiently.
Information circulation within the team is supported through article sharing and user feedback. Organizational learning is kept alive by updating content according to developing needs. The knowledge management accelerates development by automating this cycle.
Standard solutions for common problems are collected on a single platform. In this way, consistent, accurate and fast information can be presented. knowledge management directly affects user satisfaction and service quality.
Each knowledge article is tracked through version control, and it can be tracked by whom it was created or updated. This prevents the spread of misinformation and clarifies areas of responsibility. This transparency increases the reliability and accuracy of the knowledge management system.
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Frequently asked questions, guide contents and technical solutions are systematically collected in one place. This structure provides quick access for both technical teams and end users. In Knowledge Base processes, this database is the cornerstone of operational speed.
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
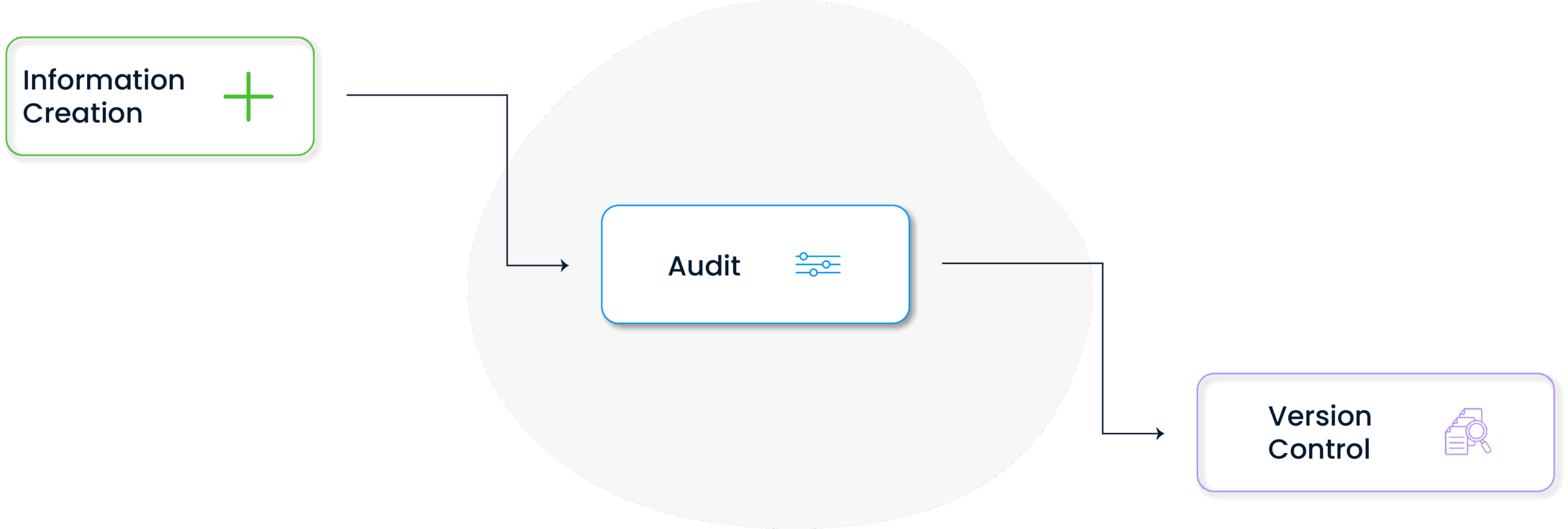
Each information article is included in the system through specific quality control and approval processes.
The content is reviewed for technical accuracy and then evaluated by authorized editors for suitability for publication. As published articles may become outdated over time, they are supported by version control and archiving systems. Thanks to this systematic approach, the knowledge management process becomes both transparent and sustainable.
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Keyword, tag or category based search options are offered.
Users can access the information they need in seconds. Effective search infrastructure plays a key role in making the knowledge management userfriendly.
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
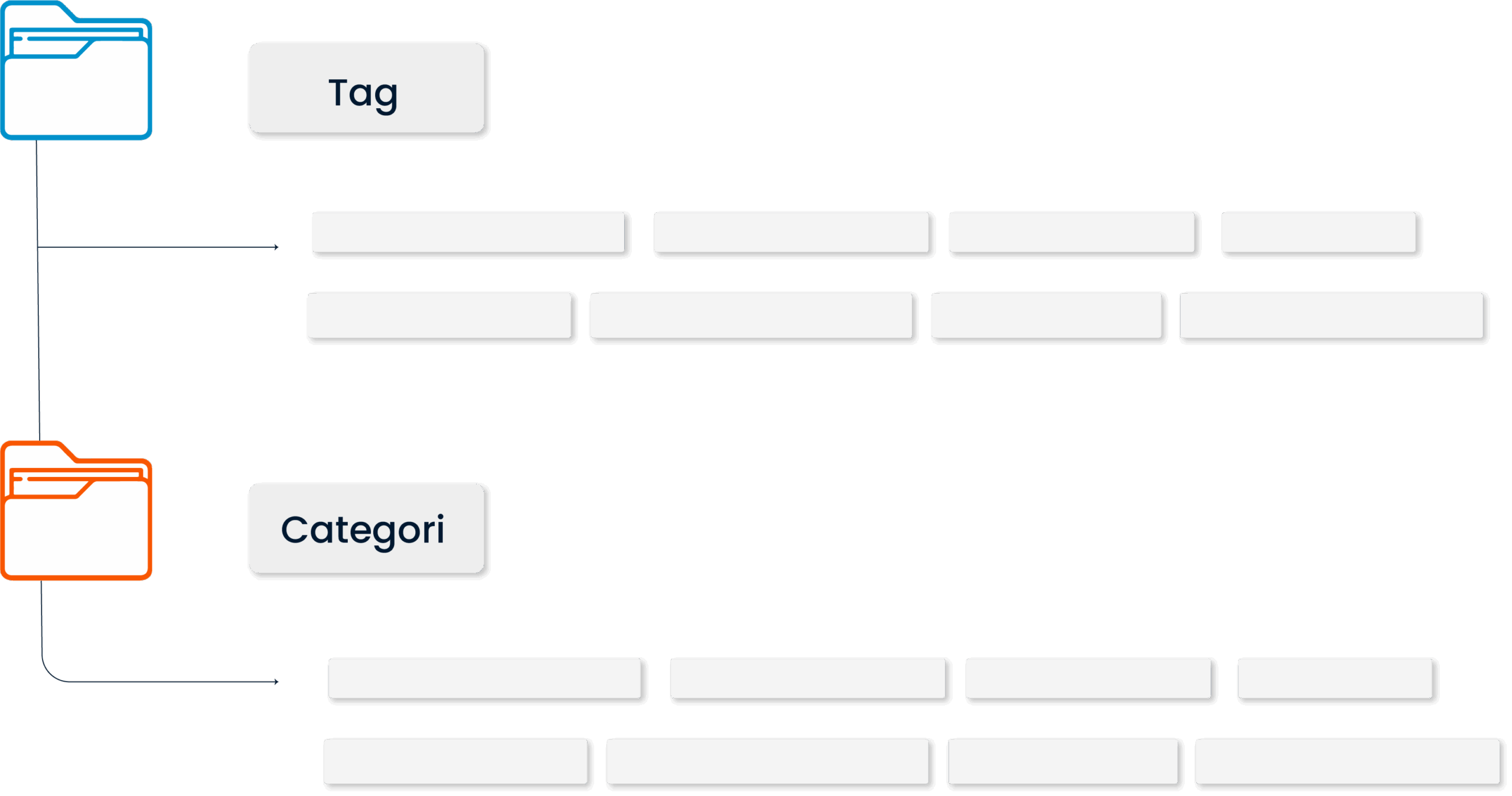
Information is categorized in a logical structure according to topics, product groups, service titles or user roles. Thanks to this structure, users can access the information they are looking for much faster and easier, while the content becomes more meaningful as it is grouped according to its context.
The tagging system strengthens the relationship between similar topics, making search results more accurate. With this structure, the knowledge management offers a content architecture that is not only organized, but also scalable and sustainable.
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
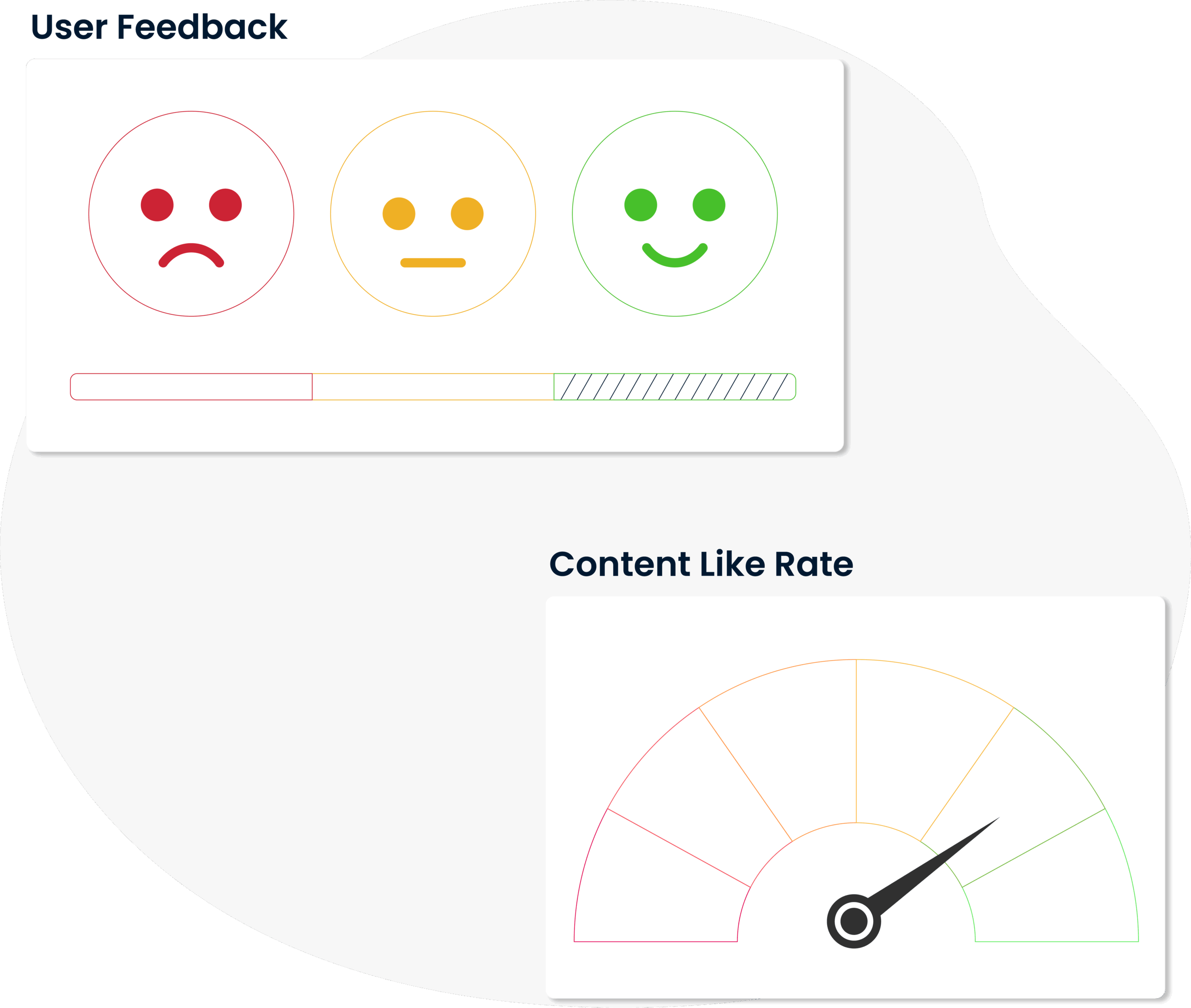
Users can contribute to content they find useful by rating it or leaving comments.
This feedback helps to identify which articles are effective or need to be updated. In the Knowledge management system, the quality cycle is supported by user contributions.

Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Users can access solution articles to solve their technical problems without contacting IT.
They are encouraged to create their own solutions with video content, step-by-step guides and interactive tutorials. This portal demonstrates the user-centered side of the knowledge management approach.

Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Warning: Undefined array key "background_image" in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 87
Warning: Trying to access array offset on null in /home/spidya/htdocs/spidya.com/wp-content/plugins/elementor/includes/conditions.php on line 90
Knowledge articles are reviewed periodically and outdated information is archived.
Every update is versioned and past changes are recorded. This feature is critical for audit, reliability and timeliness in knowledge management.

Collecting all technical knowledge and experience in a central knowledge management prevents information loss within the organization. Even new team members can adapt quickly by accessing past incidents and solution methods. This approach makes knowledge management processes sustainable.

Users can directly access guide articles to solve their problems. This reduces support requests and eases the burden on IT teams. In this way, the knowledge management enables both end users and technical teams to use their time efficiently.

Information circulation within the team is supported through article sharing and user feedback. Organizational learning is kept alive by updating content according to developing needs. The knowledge management accelerates development by automating this cycle.

Standard solutions for common problems are collected on a single platform. In this way, consistent, accurate and fast information can be presented. Knowledge management directly affects user satisfaction and service quality.

Each knowledge article is tracked through version control, and it can be tracked by whom it was created or updated. This prevents the spread of misinformation and clarifies areas of responsibility. This transparency increases the reliability and accuracy of the knowledge management system.
Features of the Knowledge Base Module
Article Management
Categorization and Tagging

Self-Service Portal




Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A knowledge base system provides quick solutions to recurring problems by preserving corporate memory. In this way, IT teams have easy access to information and problems experienced by users are solved with fewer support requests. At the same time, productivity increases by preventing information loss.
Guides, problem resolution steps, system configuration notes and video tutorials are the main contents of the knowledge library. Frequently asked questions, precautions against incorrect operations and new system announcements can also be added. Keeping this content up-to-date is critical to the success of the knowledge library.
You can access guide articles by typing keywords related to the topic you need through the portal. You can also easily access category lists or popular content. This system makes the users’ problem-solving process independent.
They are prepared by IT support teams, system administrators or designated expert users. Each article is published after going through a quality control and approval process. This process increases content reliability in the knowledge library.
Yes. Users can contribute by rating or commenting on content they find useful. Users with certain authorizations can also suggest new content or update existing articles.
Content is regularly reviewed according to technological developments or service changes. User feedback and performance reports are also taken into account in these updates. The knowledge library thus always remains up-to-date and functional.
If You Have Any Other Questions, Contact Us!
A knowledge base provides quick solutions to recurring problems by preserving corporate memory. In this way, IT teams have easy access to information and problems experienced by users are solved with fewer support requests. At the same time, productivity increases by preventing information loss.
Guides, problem resolution steps, system configuration notes and video tutorials are the main contents of the knowledge library. Frequently asked questions, precautions against incorrect operations and new system announcements can also be added. Keeping this content up-to-date is critical to the success of the knowledge library.
You can access guide articles by typing keywords related to the topic you need through the portal. You can also easily access category lists or popular content. This system makes the users’ problem-solving process independent.
They are prepared by IT support teams, system administrators or designated expert users. Each article is published after going through a quality control and approval process. This process increases content reliability in the knowledge library.
Yes. Users can contribute by rating or commenting on content they find useful. Users with certain authorizations can also suggest new content or update existing articles.
Content is regularly reviewed according to technological developments or service changes. User feedback and performance reports are also taken into account in these updates. The knowledge library thus always remains up-to-date and functional.